Describe the Fate Metabolism and Functions of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are one of the widely discussed topics among students of science across the world and they are simply referred by names like disaccharides monosaccharides and polysaccharides or by terms like complex carbohydrates. EbkNutrition Diet Therapy.
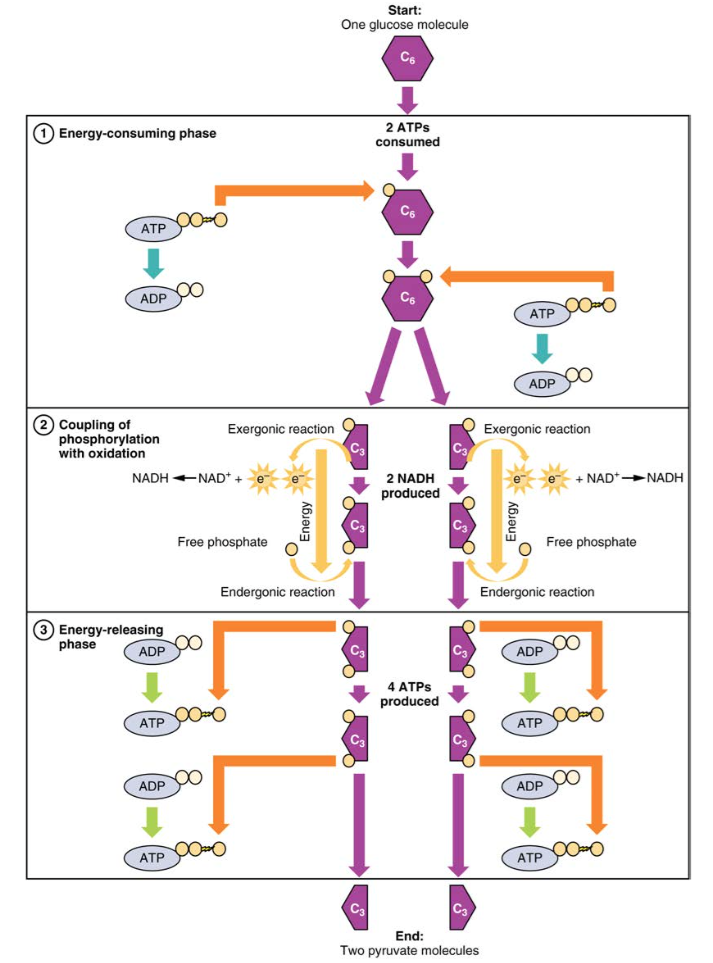
Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii
Arrow_forward Sketch the basic structures of amino acids nucleotidesmonosaccharides and fatty acids.

. Break down of molecules - for example producing energy from glucose. Simple molescule requires ATP Anabolic reaction to produce more complex molecule heat released complex molecule catabolism heat released supplies ATP. Carbohydrate metabolism - boils down to glucose metabolism.
SO 253 Describe the fate metabolism and functions of carbohydrates. Building bodys components - such as creating the phospholipids of the plasma membrane or building muscle tissue. An enzyme by name amylase assists in the breakdown of starch into glucose finally to produce energy for metabolism.
Digestion Metabolism of Carbohydrates. Our brain especially relies solely on carbohydrates for its metabolic properties. 6 Essential Functions of Carbohydrates.
The Functions of Carbohydrates in the Body There are five primary functions of carbohydrates in the human body. Carbohydrates are also known as starch simple sugars complex carbohydrates and so on. The catabolic processes of carbohydrates include.
Citric Acid Cycle 3. Sec 253 Carbohydrate Metabolism 27 Lipogenesis occurs when a More calories are consumed than required for ATP need b Less calories are consumed than required for ATP need c More cholesterol is consumed than required for ATP need d. Describe the fate metabolism and functions of carbohydrates.
They are energy production energy storage building macromolecules sparing protein and assisting in lipid metabolism. Inhibits the breakdown of proteins for energy as they are the primary source of energy. Describe briefly the fate metabolism and functions of.
Our bodies could not function without carbohydrates. 15 The net result of the complete oxidation of glucose does NOT include. Provide Us with Energy.
Easy Study Objective 1. Sec 253 Carbohydrate Metabolism 16 How many reactions take place during. Digestive fate of dietary carbohydrates.
Sec 253 Carbohydrate Metabolism Solution. SO 253 Describe the fate metabolism and functions of carbohydrates. Define the term metabolism and explain the role of ATP in anabolism and catabolism.
List the major steps in carbohydrate metabolism and note which require oxygen Describe the major steps and organs involved in lipid and protein metabolism Compare the absorptive and post-absorptive states in terms of glucose use and nutrient transport. The anabolic processes of carbohydrates include. The synthesis of glycogen from glucose which requires UTP and therefore ATP.
List several common sources of carbohydrates. Since carbohydrate utilization promotes human survival genes and traits regulating carbohydrate metabolism during exercise and energy storage have been selected throughout evolution. A water b carbon dioxide c ATP d oxygene waste heat Answer.
The ten pathwayscycles of carbohydrate metabolism are. Excess or unutilized energy is stored as fat or glycogen for later use. The main thing carbohydrates give us is the energy for metabolism.
Catabolic Processes and B. Exergonic give off energy stored in molecules. The energy released is used to power the cells and systems that make up your body.
1 Overview Of Nutrition And Health 2 Digestion And Absorption 3 Carbohydrates 4 Lipids 5 Protein 6 Metabolism Energy Balance And Body Composition 7 Weight Management 8 The Vitamins 9 Water And The Minerals 10 Fitness And. As with other food components the digestive fate of particular carbohydrates depends on their inherent chemical nature and on the supramolecular structures within foods of which they are a part. The metabolism of carbohydrates is done through two processes.
Transformation of Carbohydrates into Lipids. A Aid in glycogenesis b Inhibit gluconeogensis c Inhibit lipogenesis d Promote glycolysis e Promote gluconeogenesis Answer. Metabolic enzymes catalyze catabolic reactions that break down carbohydrates contained in food.
The goal of digestion and absorption of carbohydrates is to break them down into small molecules of sugar known as glucose. There are different ways in which carbohydrates helps living beings like storing energy in. Glucose is a primary fuel that.
It is also involved in fat metabolism and prevents ketosis. The three types of carbohydrates are. Sec 253 Carbohydrate Metabolism 22 Thyroid hormones.
1 immediate oxidation for ATP production 2 synthesis of amino acids for protein synthesis 3 synthesis of glycogen for storage in liver and skeletal muscle 4 formation of triglycerides via lipogenesis for long term storage after glycogen stores are full 5 excretion in urine if blood glucose is very high 51 What are the. Describe briefly the fate metabolism and functions of glucose lipids and proteins. Medium Study Objective 1.
Differentiate alpha and beta carbohydrates. SO 253 Describe the fate metabolism and functions of carbohydrates. HMP Pathway or Pentose Phosphate Pathway and 5.
1 Glycolysis 2 Conversion of Pyruvate to Acetyl COA 3 Citric Acid Cycle 4 Gluconeogenesis 5 Glycogen Metabolism 6 Glycogenesis 7 Glycogenolysis 8 Hexose. In most animals and in man when dietary carbohydrates are in excess the oxidation of a part of glucose maintains relatively high concentrations of ATP NADH and NADPH. 2 However current lifestyles are pre-dominantly sedentary which coupled with the intake of excessive amounts of carbohydrates has led to metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes.
Describe the fate metabolism and functions of carbohydrates. Essential functions that make carbohydrates important are as follows. Fate of glucose - glucose is the bodys preferred source for synthesizing ATP.
10 Cycles With Diagram This article throws light upon the ten major pathwayscycles of carbohydrate metabolism. Discuss the structures and functions of carbohydrates. Easy Study Objective 1.
The primary role of carbohydrates is to supply energy to all cells in the body.
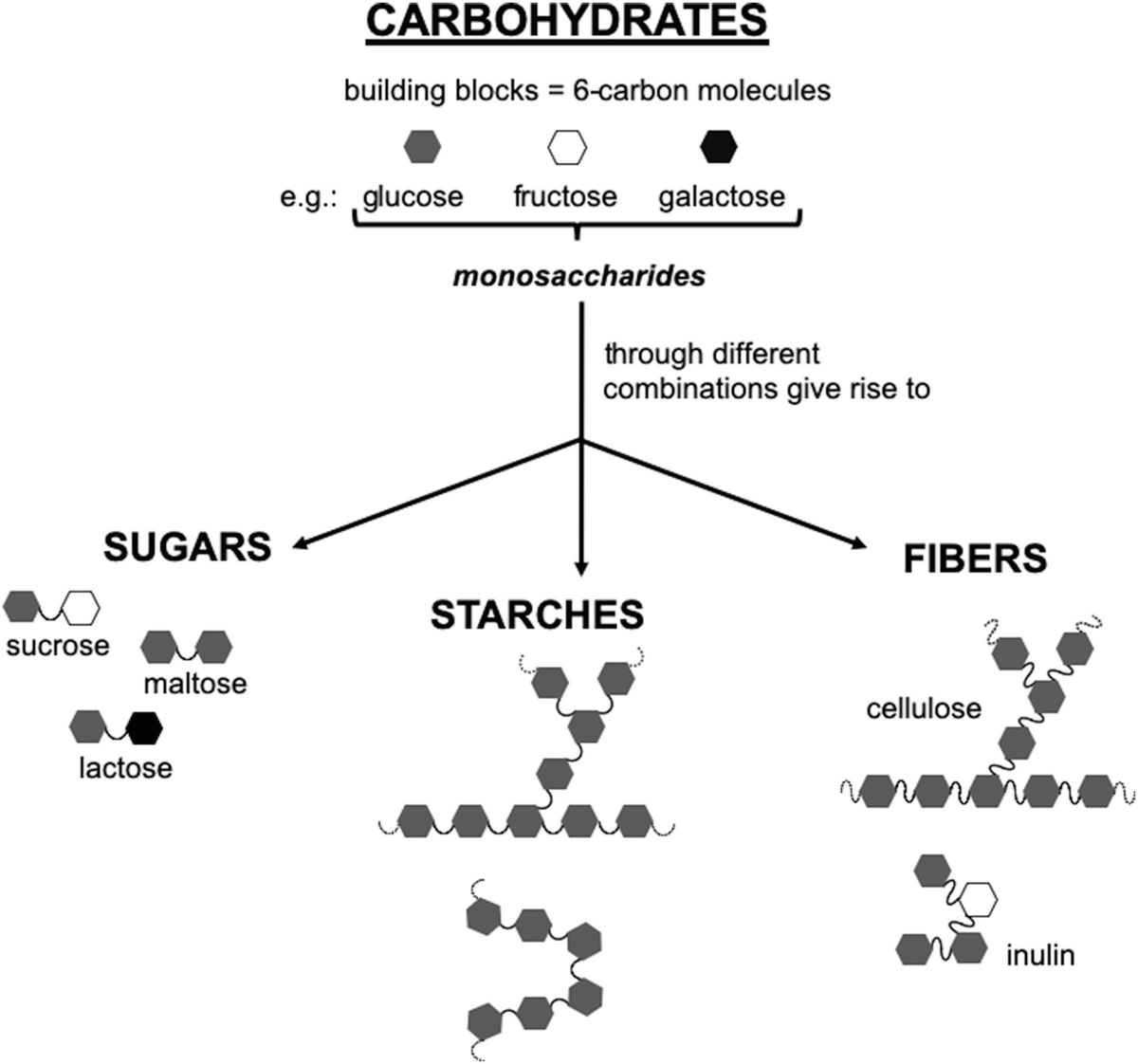
Carbohydrate Metabolism Springerlink
Connections Of Carbohydrate Protein And Lipid Metabolic Pathways Boundless Biology

Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii
What S Carbohydrate Metabolism Quora
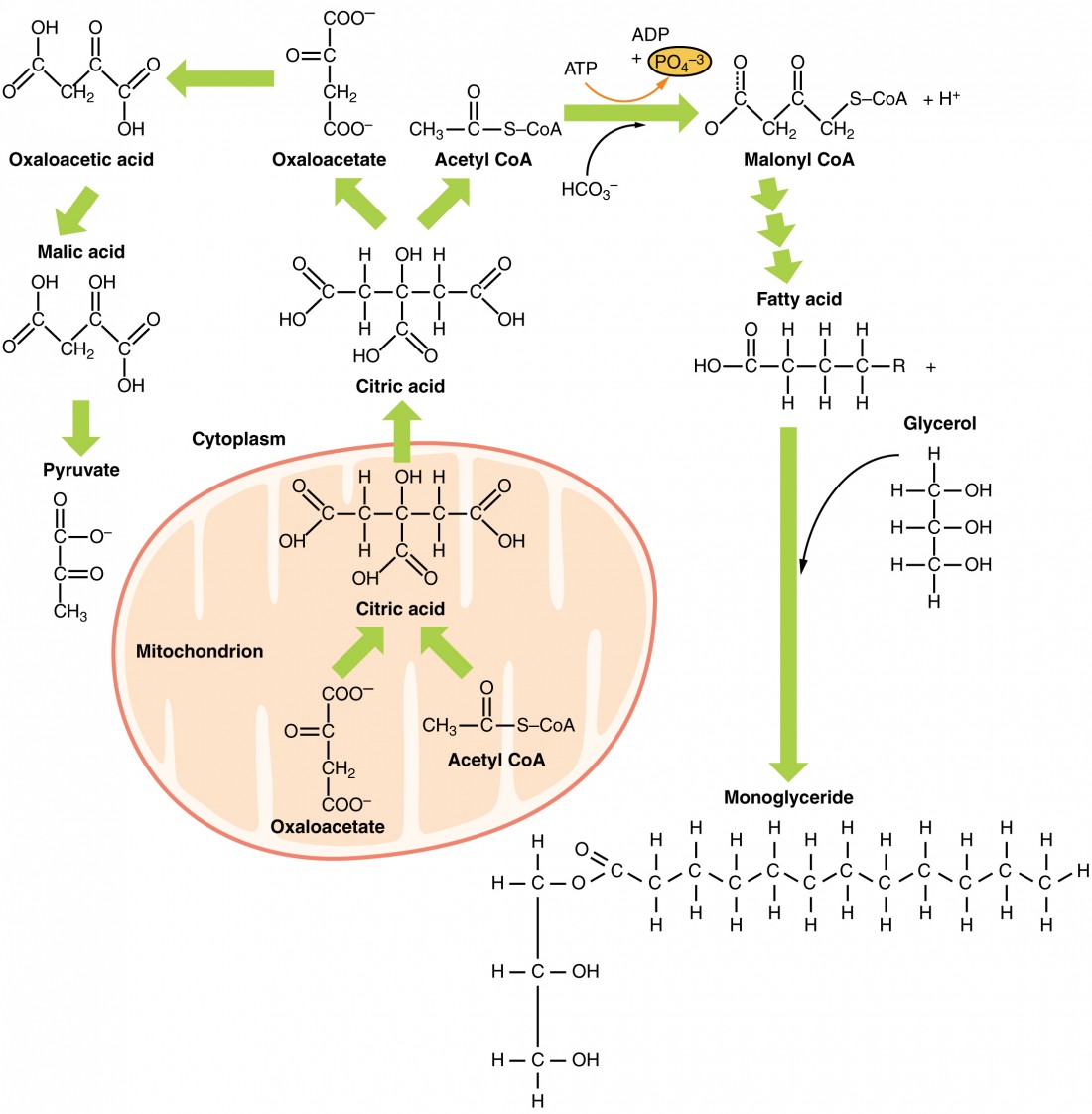
Lipid Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii

24 2 Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy Physiology
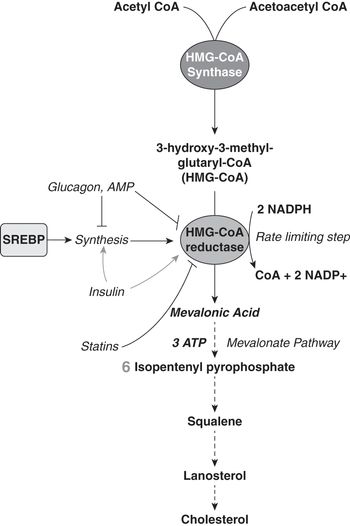
Carbohydrate Protein And Lipid Metabolism Chapter 36 Part 1 Mrcog Revision Notes And Sample Sbas
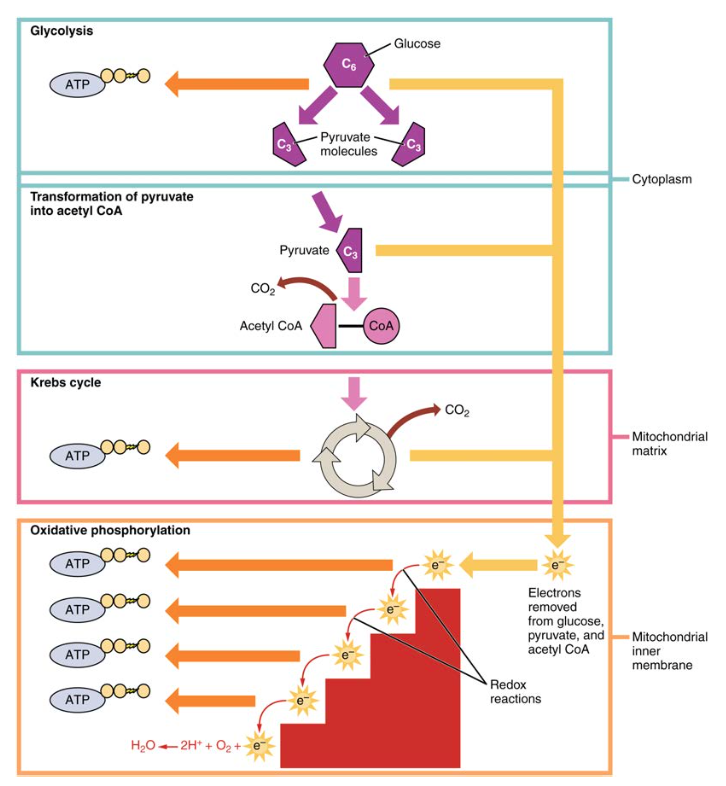
Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii
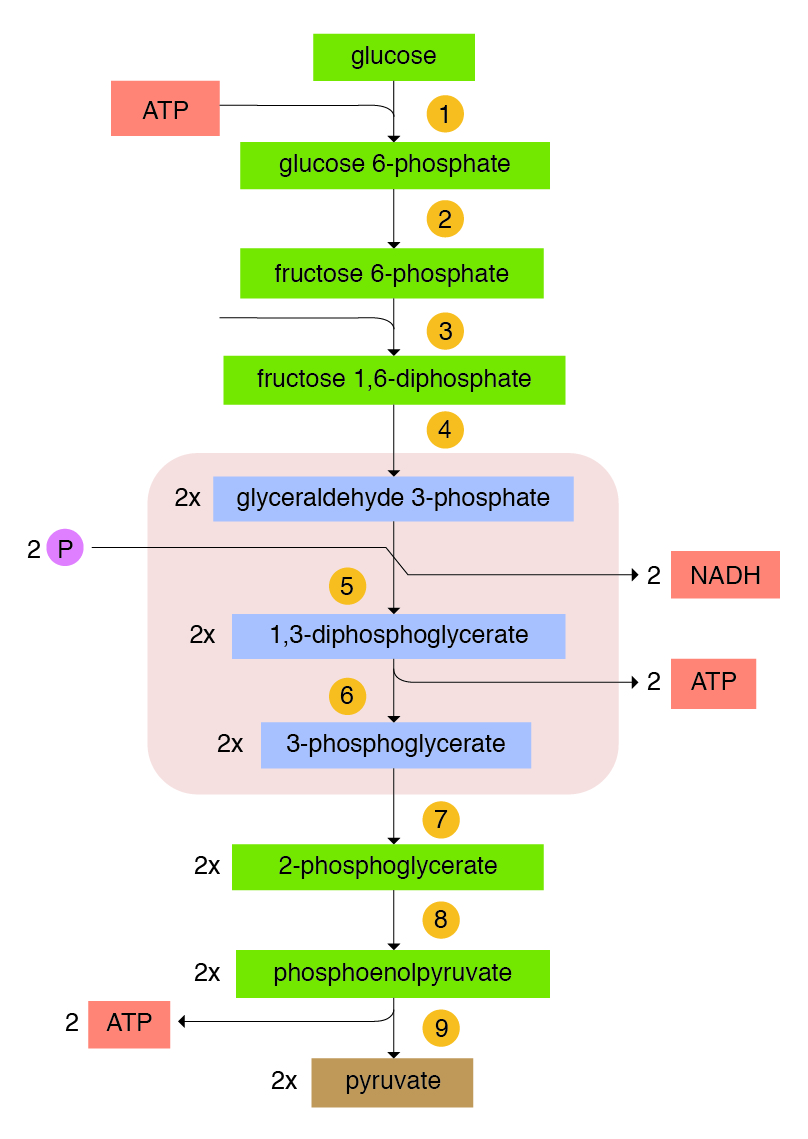
V Carbohydrates Metabolism A Guide To The Principles Of Animal Nutrition
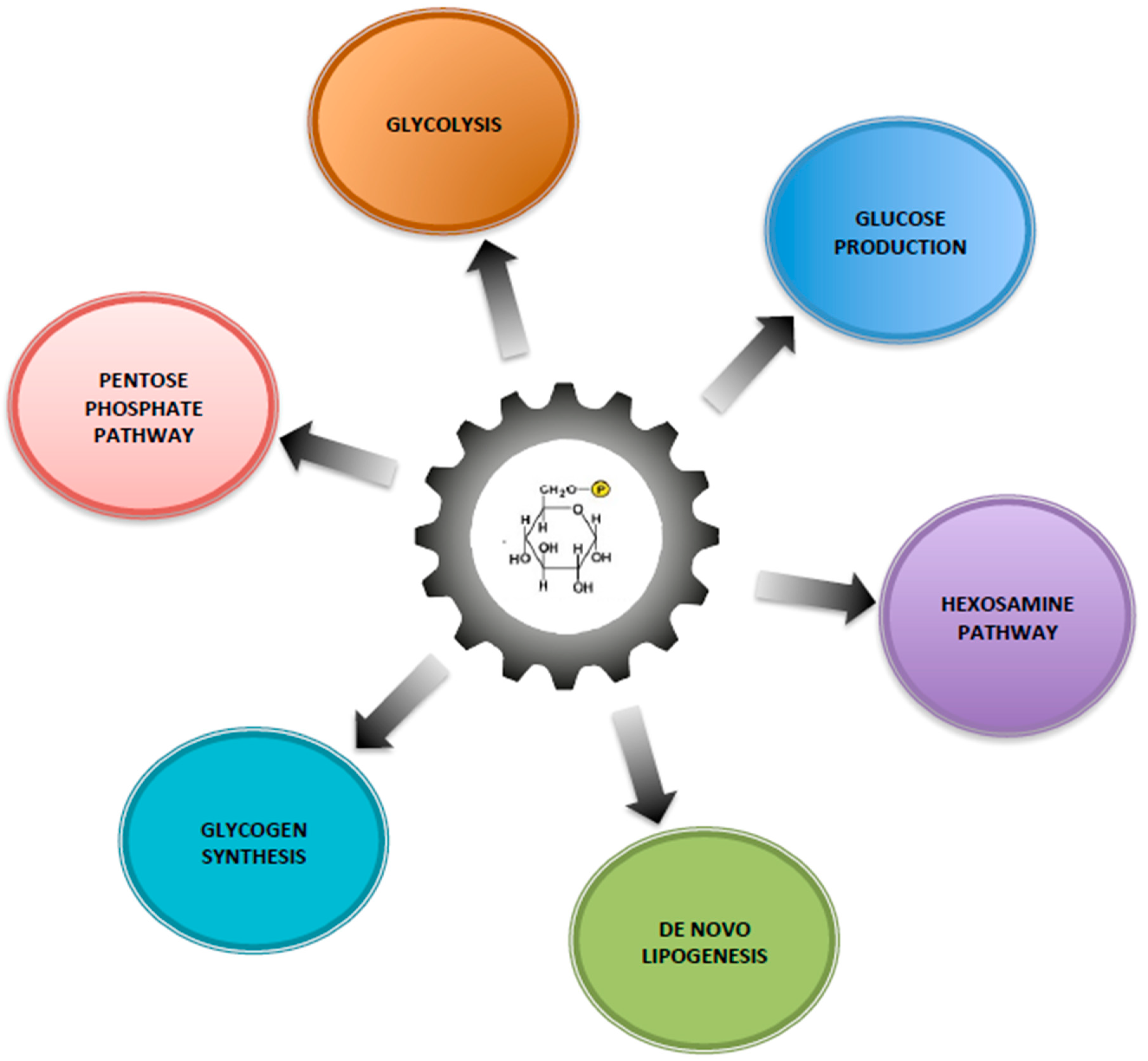
Metabolites Free Full Text Glucose 6 Phosphate A Central Hub For Liver Carbohydrate Metabolism Html
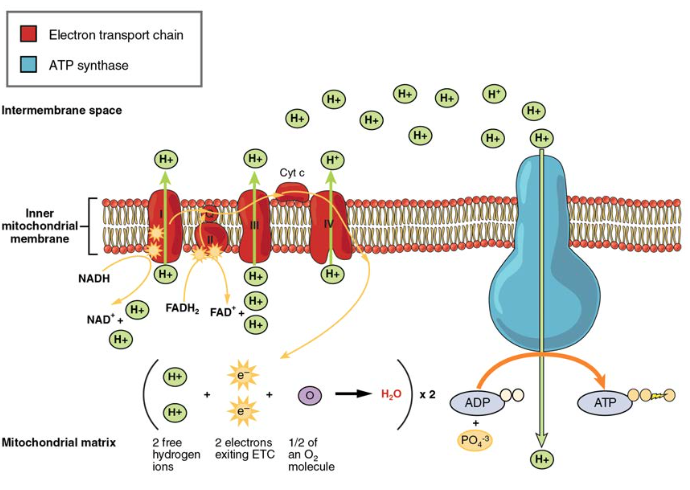
Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii
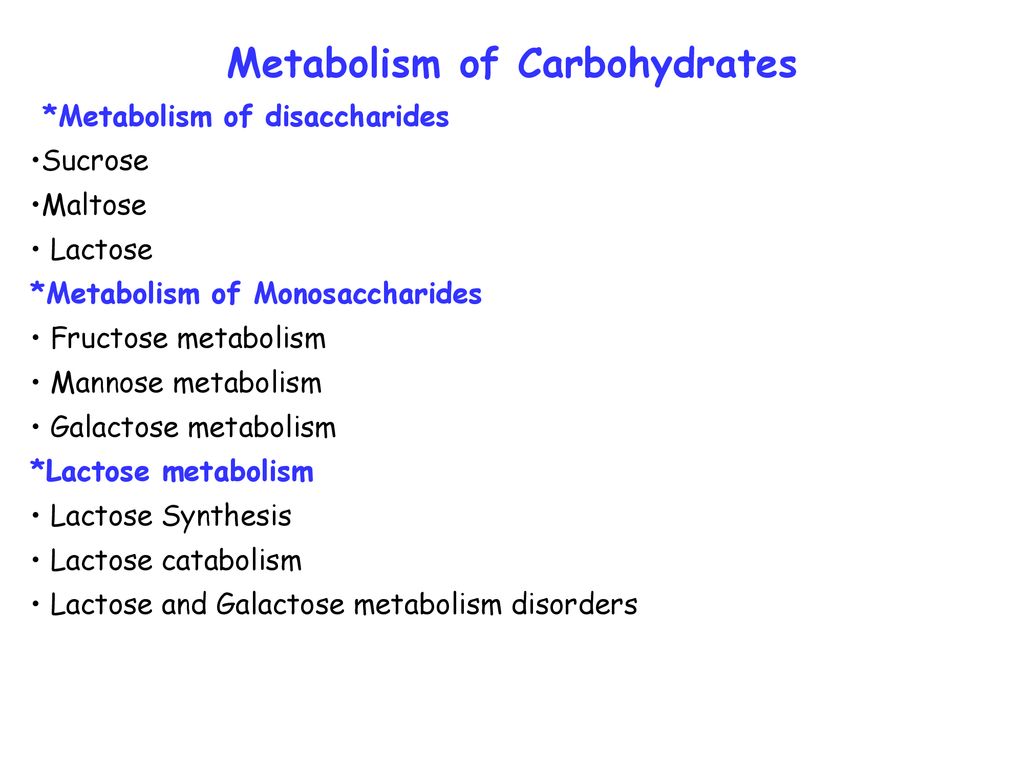
Metabolism Of Carbohydrates Ppt Download

Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii

Influence Of Insulin And Ppara On Carbohydrate Metabolic Pathways Download Scientific Diagram
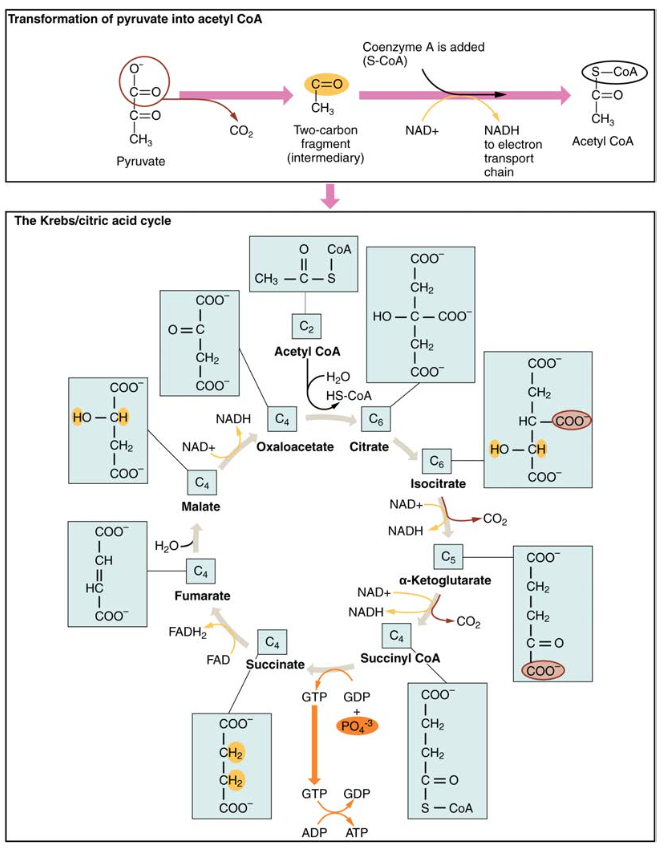
Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii
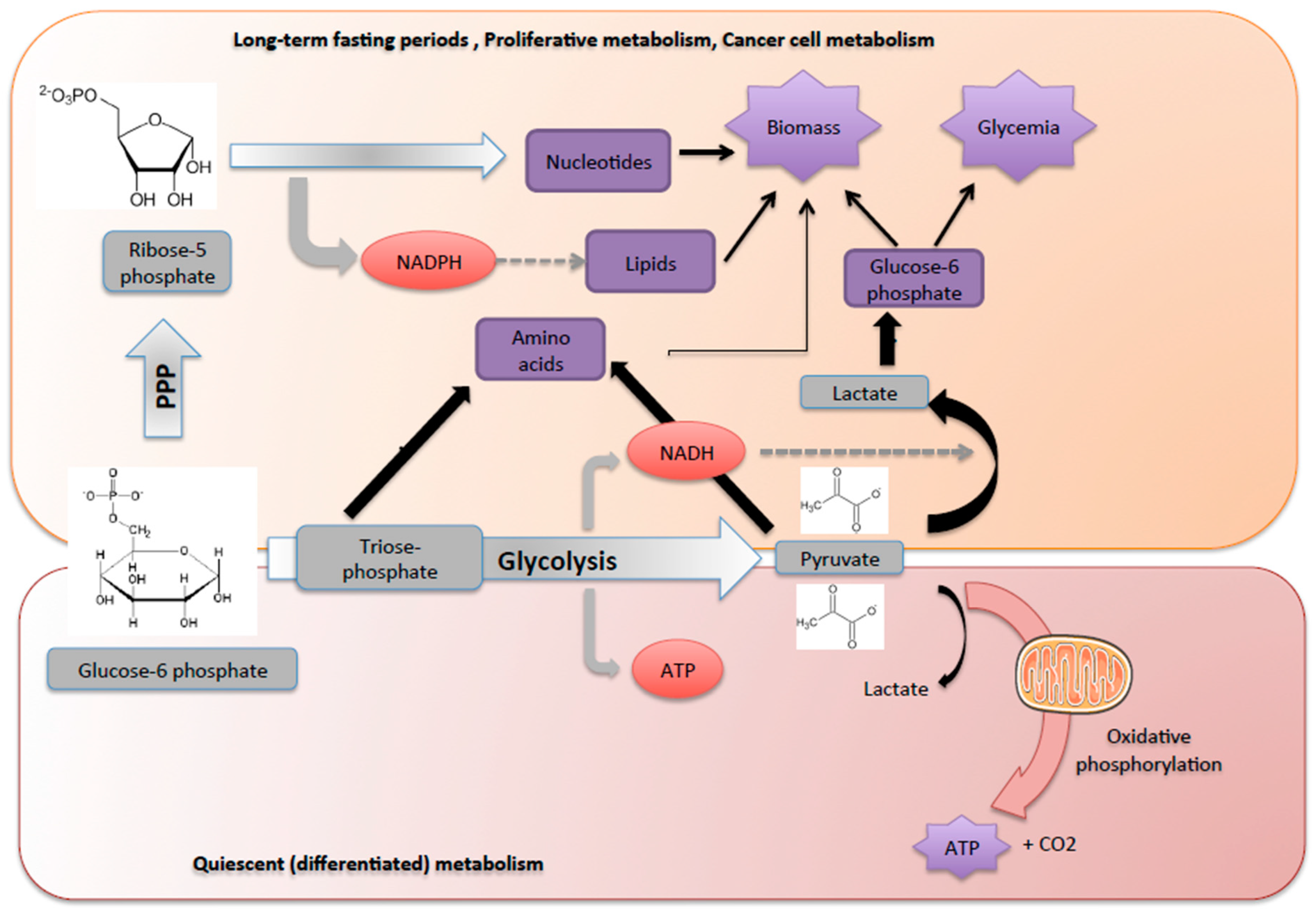
Metabolites Free Full Text Glucose 6 Phosphate A Central Hub For Liver Carbohydrate Metabolism Html
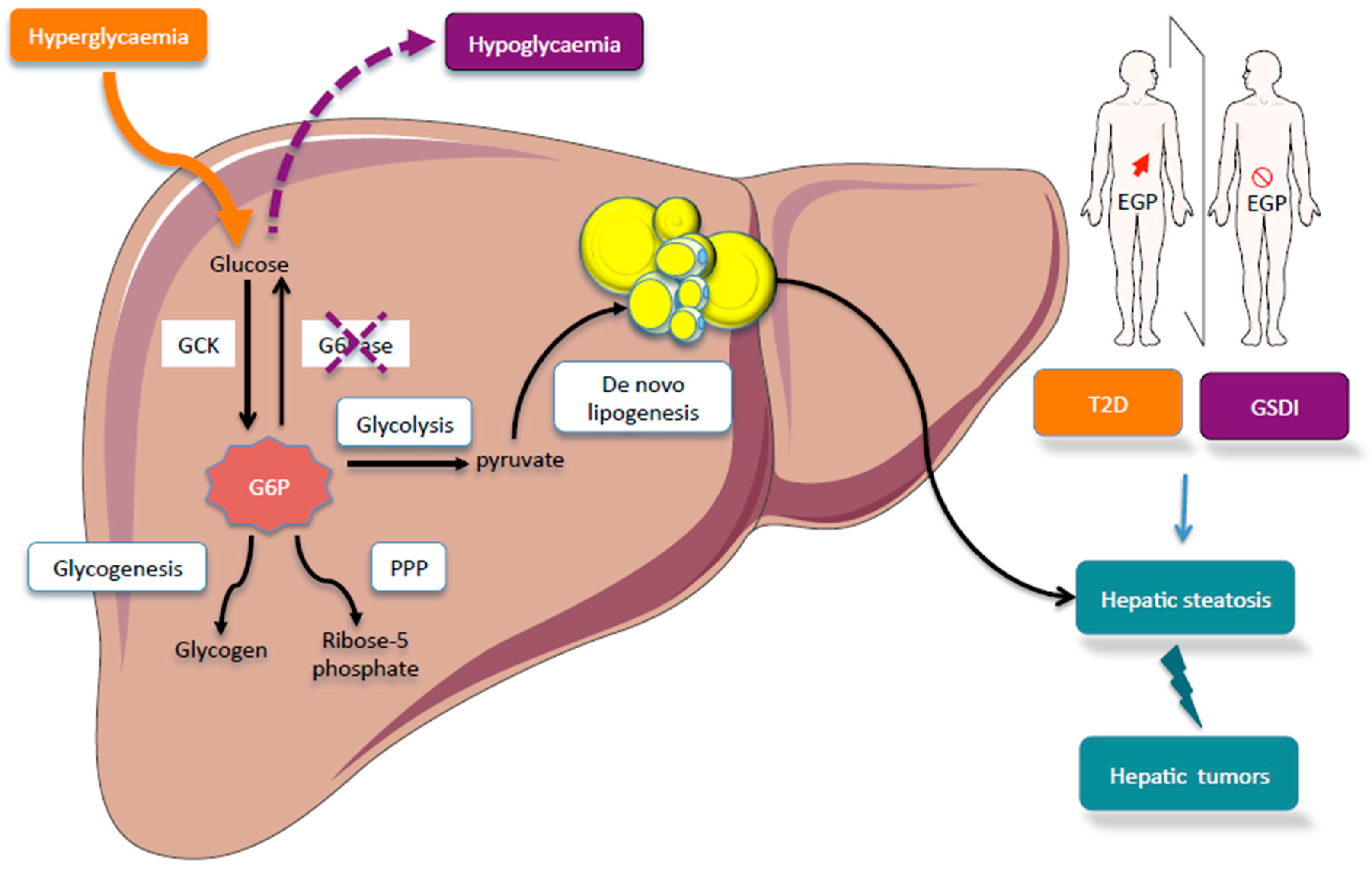
Metabolites Free Full Text Glucose 6 Phosphate A Central Hub For Liver Carbohydrate Metabolism Html

Connections Of Carbohydrate Protein And Lipid Metabolic Pathways Boundless Biology

Comments
Post a Comment